receding gums
Causes, symptoms, therapies, prevention.
In the following I will describe the causes that can lead to gum recession, how they can be largely avoided and how they can be treated with modern methods
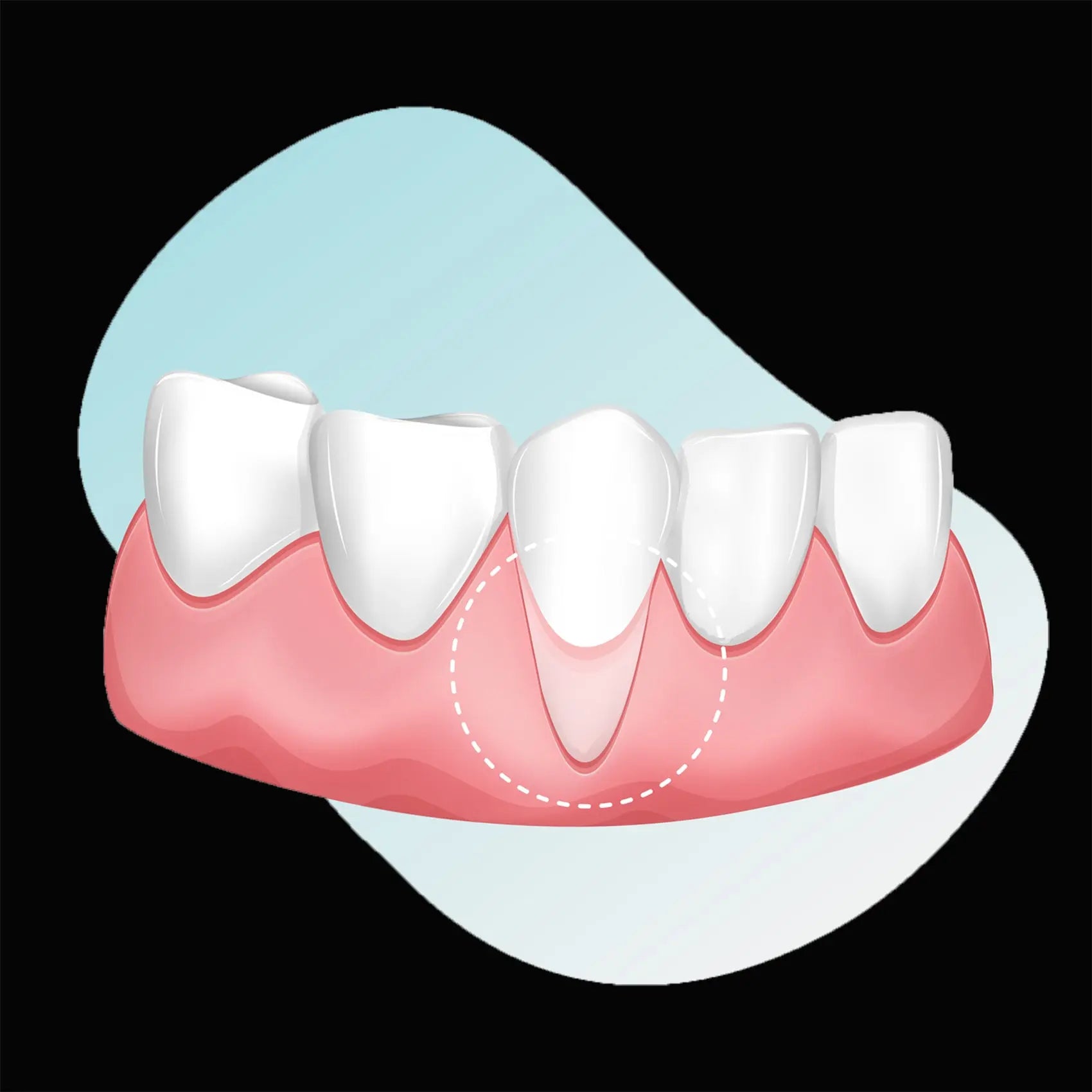
Receding gums, also known as recession, mean a loss of gums beyond the crown portion of the tooth. It is a disease of the periodontal ligament and therefore affects not only the gums but also the bone surrounding the teeth. This results in exposed parts of the tooth root.

Causes:
Various factors can play a decisive role in the development of gum recession:
- Incorrect brushing technique and overly aggressive cleaning products: if a cross-direction brushing technique is used incorrectly (scrubbing) or if brushes and cleaning products that are too hard and aggressive are used, small injuries to the gum line are repeatedly produced. If the gum line continues to be injured, it becomes inflamed, the underlying bone is broken down and the gums recede.
- Functional overload (pressing and grinding): Incorrect loading of the teeth often occurs when there are dysfunctions of the jaw joints or malocclusion of the teeth (tilting, rotation of the teeth). Psychological stress such as stress can also lead to grinding or pressing of the teeth, which usually occurs at night. This permanent overload can lead to reduced blood flow to the gums, which can subsequently lead to gum recession.
- Lip and cheek frenulum : Lip or cheek frenulum can permanently irritate the gum line by constantly pulling on it. If you pull on the frenulum during the examination of the patient and this leads to an anemic reaction (white gingival papilla due to bloodlessness), this leads to permanent damage to the gum tissue in everyday life and, as a result, to receding gums (recession).
- Excessive or incorrect use of force during orthodontic treatment : Forced movement of the teeth can lead to recessions, especially in patients with very narrow bone surrounding the tooth. A large part of the tooth root is moved out of the tooth-supporting bone, which can subsequently lead to gum recession. At the same time, it must be mentioned that orthodontic measures can also positively support the process of covering recessions by returning teeth to the tooth-supporting bone.
- Inflammatory or degenerative processes in the gum area (periodontitis and periodontosis): Early inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) can heal without any subsequent damage if treated early. If treatment is started too late or a disease is detected too late because regular check-ups with the dentist have not taken place, periodontitis can develop. This affects not only the gums but also the bone surrounding the tooth. If the bone then breaks down due to the inflammatory changes, the gums will also recede further and a recession will occur.
Receding gums can be both painful and aesthetically detrimental. If the recession is left untreated, in the worst case scenario it can lead to the loss of the affected teeth.
If treatment is started too late or a disease is detected too late because regular check-ups with the dentist have not taken place, periodontitis can develop.
Symptoms:
The most common symptoms of gingival recession are:
- Exposed tooth necks (teeth that appear longer)
- Sensitive teeth (pain from heat, cold, sweet and sour foods)
- Possible loss of the gums that are firmly attached to the tooth
- Possible loss of tooth hard substance in the area of the exposed root surface
Therapies:
Regardless of the surgical treatment chosen, any existing inflammatory changes must be eliminated prior to any treatment to eliminate gum recession. In addition, incorrect loading of the teeth must be treated and the patient must be shown the correct brushing technique and cleaning products as part of oral hygiene instructions. Furthermore, the patient should be motivated to enter a recall program with regular check-ups tailored to the individual risk of further recession and inflammation.
To treat receding gums (recessions), various surgical methods are available, adapted to the extent of the recession.
- Coronary flap (with or without free connective tissue graft)
With this technique, the gums below the recession are moved upwards towards the tooth crown using special surgical procedures and fixed with stitches. This way, the portion of the resulting gum recession can be covered.
In patients with a thin gum type, this technique can be combined with a free connective tissue graft. This can thicken the gums and subsequently make them more stable against new recessions.
- removal of a free connective tissue transplant
As a rule, the connective tissue is removed from the side of the palate. Using magnifying glasses or microscopes, a portion of tissue can be removed microsurgically directly beneath the palate mucosa. This small procedure allows sufficient connective tissue to be obtained. The wounds then heal mostly without irritation and pain.
- tunnel technique to cover receding gums
This technique completely avoids the need for incisions within the gums to relieve pressure. This means that completely scar-free results can be achieved. This technique can also be used to treat several adjacent recessions without any problem.
Put simply, this technique involves preparing a "bag" deep in the gums, starting from the point where the gums are receding. The gingival papillae between the individual teeth remain intact. If there are several recessions next to each other, the prepared "bags" can be connected underground in the form of a tunnel. The free connective tissue transplant removed as described above can now be inserted into the space created. The gums are then fixed at the new level covering the recession with fine sutures.
Prevention: what does SNOW PEARL offer
Because incorrect brushing technique and overly aggressive cleaning products play a significant role in the development of receding gums, SNOW PEARL has created toothpastes that eliminate this risk factor. The KONEX HD filaments used in all SNOW PEARL toothbrushes are extremely soft and gentle, they allow efficient and thorough cleaning, massage the gums at the same time and promote healthy blood circulation without causing injury or irritation. The filaments are also very elastic and dimensionally stable, do not bend and are very durable. At their tip they are 8 times thinner than that of other normal soft filaments, their optimized density allows them to glide deep into the gaps and slightly below the gum line, providing excellent cleaning even there. This combination makes this generation of toothbrushes unbeatable.